Okabe and El Psy Kongroo
题目描述
你在 $(0,0)$ 。
在 $(x,y)$ 时,每次移动可以到达 $(x+1,y+1),(x+1,y),(x+1,y-1)$ 。
平面上有 $n$ 条线段,平行于 $x$ 轴,参数为$a_i$ , $b_i$ ,$c_i$ ,表示在 $(a_i,c_i)$ 到 $(b_i,c_i)$ 的一条线段,保证 $b_i=a_{i+1}$。
要求你一直在线段的下方且在 $x$ 轴上方,即 $a_i \leq x \leq b_i$ 时, $0 \leq y \leq c_i$ 。
问 $:$ 到达 $(k,0)$ 的方案数,方案数对 $10^9+7$ 取模。
$n \leq 100 , k \leq 10^{18} , c_i \leq 15$
输入格式
第一行包含整数 $n$ 和 $k$ ( $ 1 \leq n \leq 100 $ , $ 1 \leq k \leq 10^{18} $ ), 表示线段数和终点的横坐标
下面 $n$ 行每行包含三个整数 $ a_{i} $ , $ b_{i} $ , $ c_{i} $ ( $ 0\leq a_{i}\leq b_{i}\leq 10^{18} $ , $ 0 \leq c_{i} \leq 15 $ ), 表示每个线段的左端点, 右端点, 和它的纵坐标
保证 $ a_{1}=0 $ , $ a_{n} \leq k \leq b_{n} $ , $ a_{i}=b_{i-1} $.
输出格式
问 $:$ 到达 $(k,0)$ 的方案数,方案数对 $10^9+7$ 取模。
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
| |
样例输出 #1
| |
样例 #2
样例输入 #2
| |
样例输出 #2
| |
提示
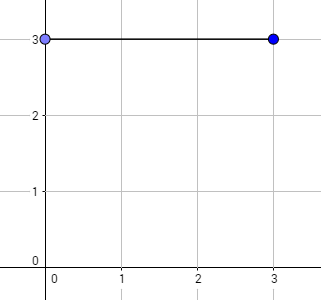
The graph above corresponds to sample 1. The possible walks are:
$$ (0, 0) \rightarrow (1, 0) \rightarrow (2, 0) \rightarrow (3, 0) $$ $$ (0, 0) \rightarrow (1, 1) \rightarrow (2, 0) \rightarrow (3, 0) $$ $$ (0, 0) \rightarrow (1, 0) \rightarrow (2, 1) \rightarrow (3, 0) $$ $$ (0, 0) \rightarrow (1, 1) \rightarrow (2, 1) \rightarrow (3, 0) $$
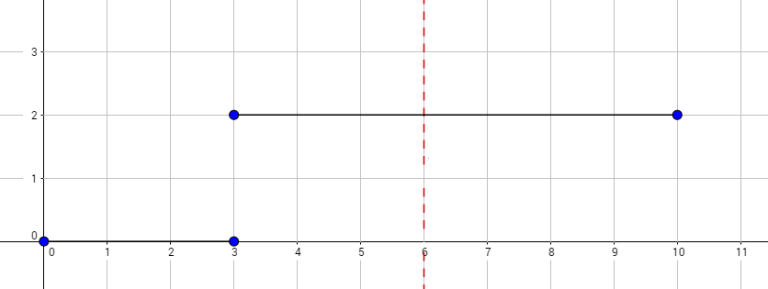
The graph above corresponds to sample 2. There is only one walk for Okabe to reach $ (3,0) $ . After this, the possible walks are:
$$ (3, 0) \rightarrow (4, 0) \rightarrow (5, 0) \rightarrow (6, 0) $$ $$ (3, 0) \rightarrow (4, 0) \rightarrow (5, 1) \rightarrow (6, 0) $$ $$ (3, 0) \rightarrow (4, 1) \rightarrow (5, 0) \rightarrow (6, 0) $$ $$ (3, 0) \rightarrow (4, 1) \rightarrow (5, 1) \rightarrow (6, 0) $$
题解
本题递推方程
$$ dp_{x,y} = dp_{x-1, y-1} + dp_{x-1, y} + d_{x-1, +y1} $$
然而 $k$ 的范围是 $ 1 \leq k \leq 10^{18} $, 递推会 TLE ! 所以很容易想到要用矩阵加速递推
对所有 $x$, 列出所有 $y \in [0, c_i]$ 的递推关系 $:$
$$ dp_{x, 0} = dp_{x-1, 0} + dp_{x-1, 1} \newline dp_{x, 1} = dp_{x-1, 0} + dp_{x-1, 1} + dp_{x-1, 1} \newline dp_{x, 2} = dp_{x-1, 1} + dp_{x-1, 2} + dp_{x-1, 3} \newline \vdots \newline dp_{x, c_i-1} = dp_{x-1, c_i-2} + dp_{x-1, c_i-1} + dp_{x-1, c_i} \newline dp_{x, c_i} = dp_{x-1, c_i-1} + dp_{x-1, c_i} $$
写出其矩阵形式
$$ \begin{bmatrix} dp_{x, 0} \newline dp_{x, 1} \newline dp_{x, 2} \newline dp_{x, 3} \newline dp_{x, 4} \newline \vdots \newline dp_{x, c_i-2} \newline dp_{x, c_i-1} \newline dp_{x, c_i} \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} \textcolor{red}{1} & \textcolor{red}{1} & 0 & 0 & \cdots & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \newline \textcolor{red}{1} & \textcolor{red}{1} & \textcolor{red}{1} & 0 & \cdots & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \newline 0 & \textcolor{red}{1} & \textcolor{red}{1} & \textcolor{red}{1} & \cdots & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \newline 0 & 0 & \textcolor{red}{1} & \textcolor{red}{1} & \cdots & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \newline 0 & 0 & 0 & \textcolor{red}{1} & \cdots & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \newline \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \newline 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & \cdots & \textcolor{red}{1} & \textcolor{red}{1} & 0 & 0 \newline 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & \cdots & \textcolor{red}{1} & \textcolor{red}{1} & \textcolor{red}{1} & 0 \newline 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & \cdots & 0 & \textcolor{red}{1} & \textcolor{red}{1} & \textcolor{red}{1} \newline \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} dp_{x-1, 0} \newline dp_{x-1, 1} \newline dp_{x-1, 2} \newline dp_{x-1, 3} \newline dp_{x-1, 4} \newline \vdots \newline dp_{x-1, c_i-2} \newline dp_{x-1, c_i-1} \newline dp_{x-1, c_i} \end{bmatrix} $$
其中, 第二个矩阵大小为 $(c_i+1) * (c_i+1)$
所以, 对 $\forall i \in [1, n]$, 都有
$$ \begin{bmatrix} dp_{b_i, 0} \newline dp_{b_i, 1} \newline dp_{b_i, 2} \newline dp_{b_i, 3} \newline dp_{b_i, 4} \newline \vdots \newline dp_{b_i, c_i-2} \newline dp_{b_i, c_i-1} \newline dp_{b_i, c_i} \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} \textcolor{red}{1} & \textcolor{red}{1} & 0 & 0 & \cdots & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \newline \textcolor{red}{1} & \textcolor{red}{1} & \textcolor{red}{1} & 0 & \cdots & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \newline 0 & \textcolor{red}{1} & \textcolor{red}{1} & \textcolor{red}{1} & \cdots & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \newline 0 & 0 & \textcolor{red}{1} & \textcolor{red}{1} & \cdots & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \newline 0 & 0 & 0 & \textcolor{red}{1} & \cdots & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \newline \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \newline 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & \cdots & \textcolor{red}{1} & \textcolor{red}{1} & 0 & 0 \newline 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & \cdots & \textcolor{red}{1} & \textcolor{red}{1} & \textcolor{red}{1} & 0 \newline 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & \cdots & 0 & \textcolor{red}{1} & \textcolor{red}{1} & \textcolor{red}{1} \newline \end{bmatrix} ^ {b_i - a_i} \begin{bmatrix} dp_{a_i-1, 0} \newline dp_{a_i-1, 1} \newline dp_{a_i-1, 2} \newline dp_{a_i-1, 3} \newline dp_{a_i-1, 4} \newline \vdots \newline dp_{a_i-1, c_i-2} \newline dp_{a_i-1, c_i-1} \newline dp_{a_i-1, c_i} \end{bmatrix} $$
所以只要记录对 $ \forall i \in [1, n-1]$ 进行矩阵快速幂后的结果, 存储在 $base$ 中, 在第 $i+1$ 次循环中使用, 答案即为结果矩阵的第一个数字
Code
| |
![Featured image of post [Codeforces821E] Okabe and El Psy Kongroo](/cover/23.png)